はじめに
概略
- 位置合わせ、レジストレーションなど周辺概念について調べた
- open3d を用いて実装し、花卉の三次元点群を位置合わせした
背景
点群の位置合わせ
点群の位置合わせとは、二つの点群に対して、対応する点を推定する処理のこと
具体的な手法としては、反復最近接点 (ICP: Iterative Closest Point) アルゴリズムがよく用いられる。ICPアルゴリズムは、2つの点群の間の剛体変換(回転と並進)を求めるための手法で、これにより一方の点群を他方の点群に位置合わせする。
ICPの欠点
- データ同士の座標がある程度近くなければならない
- 誤差収束まで反復するため、場合によっては処理時間が長くなる
- あくまでも近似なため、厳密解ではない
前処理
- ボクセルグリッドにより点群密度を均一にする
- RANSACによる平面検出
レジストレーション
レジストレーションとは、複数の点群データをひとつの点群データに統合する作業のこと。
レジストレーションは位置合わせと同義かと思っており、登録という意味のregistrationという単語がなぜ使われているのかと思っていたが納得。
やり方
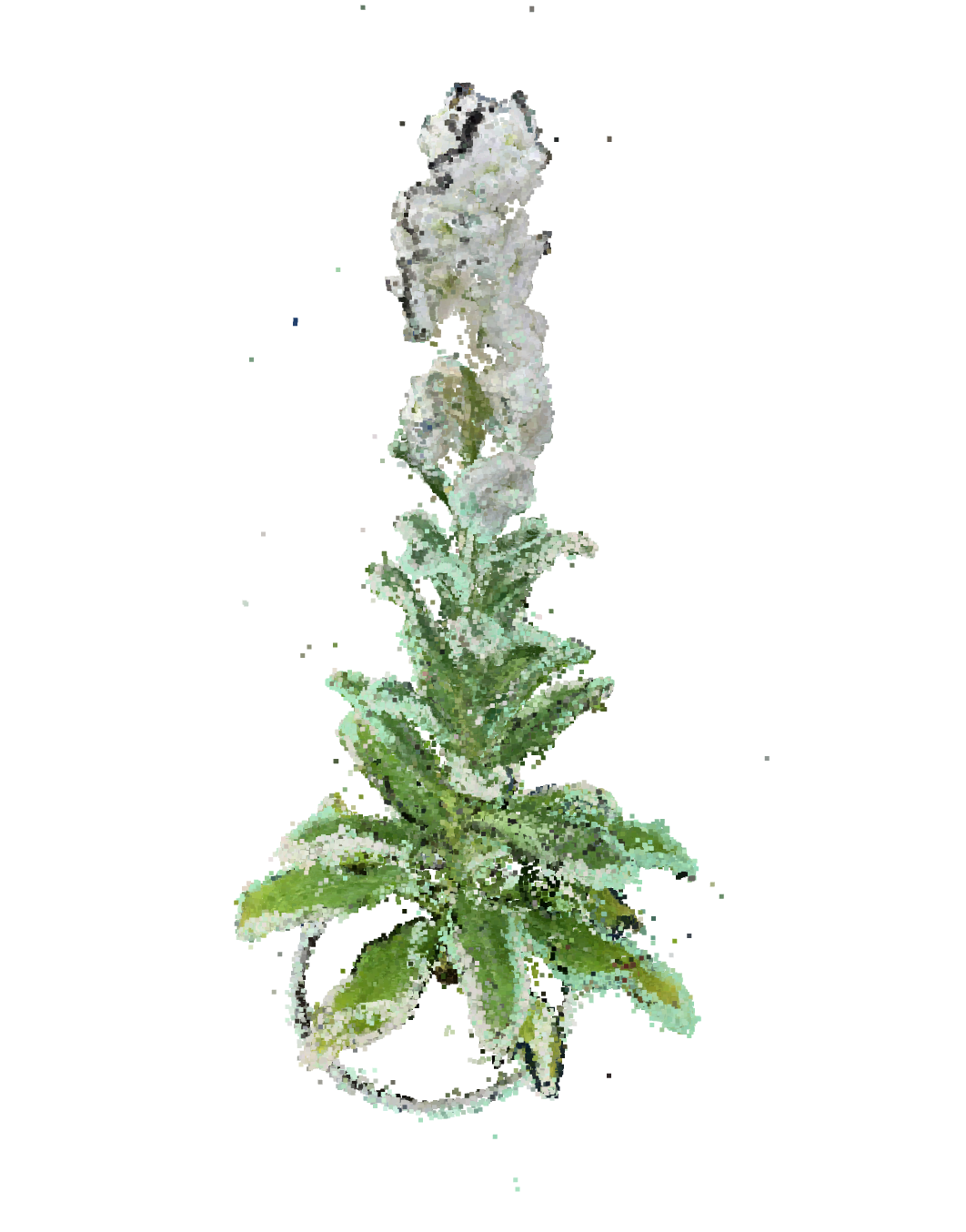

- 上のようなストックを対象として、2回三次元計測をした
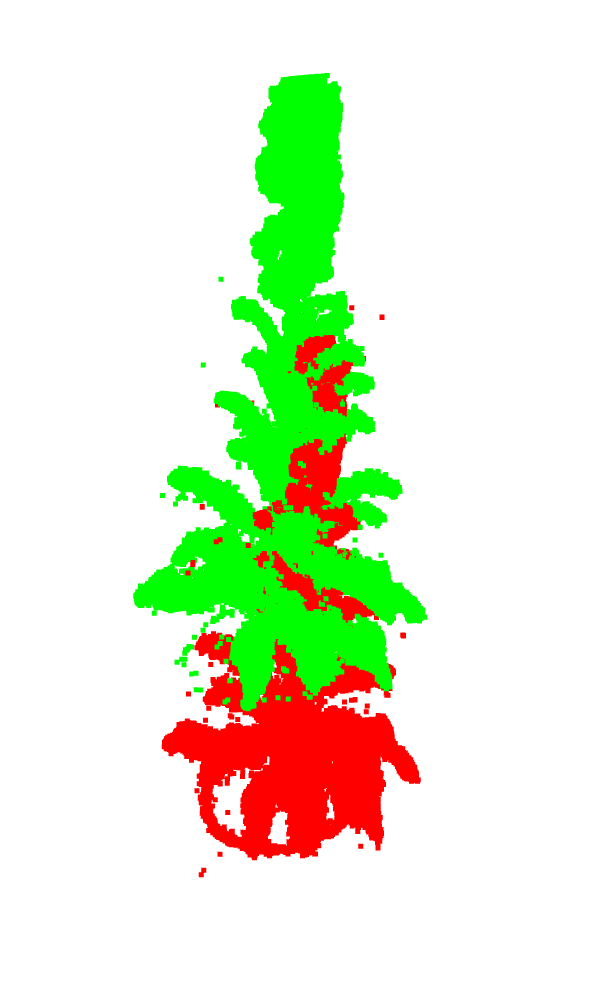
- 初期ではこれほどズレがあった
モジュール
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
import copy
import csv
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
大まかな流れ
def main(inputfile,input_accurate):
pcd_tar = o3d.io.read_point_cloud( f"model/{inputfile}" )
pcd_acc = o3d.io.read_point_cloud( f"model/{input_accurate}")
voxel_size = 0.01
source_down, source_fpfh = preprocess_point_cloud(pcd_tar, voxel_size)
target_down, target_fpfh = preprocess_point_cloud(pcd_acc, voxel_size)
print("finish preprocess")
result_ransac = execute_global_registration(source_down, target_down,
source_fpfh, target_fpfh,
voxel_size,True)
print("finish ransac")
global_reg_pcd = copy.deepcopy(pcd_tar).transform(result_ransac.transformation)
print("start local reg")
source_down, source_fpfh = preprocess_point_cloud(global_reg_pcd, voxel_size)
target_down, target_fpfh = preprocess_point_cloud(pcd_acc, voxel_size)
threshold = 0.02
result= execute_local_registration(source_down,target_down,threshold)
trans_reg = result.transformation
pcd_reg = copy.deepcopy(global_reg_pcd).transform(trans_reg)
print("finish local reg")
- 前処理
- ransacを用いたグローバルな位置合わせ
- 前処理
- icpアルゴリズムを用いたローカルな位置合わせ
前処理
def preprocess_point_cloud(pcd, voxel_size ):
print(":: Downsample with a voxel size %.3f." % voxel_size)
pcd_down = pcd.voxel_down_sample(voxel_size)
radius_normal = voxel_size * 2
print(":: Estimate normal with search radius %.3f." % radius_normal)
pcd_down.estimate_normals(
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius_normal, max_nn=30))
radius_feature = voxel_size * 10
print(":: Compute FPFH feature with search radius %.3f." % radius_feature)
pcd_fpfh = o3d.pipelines.registration.compute_fpfh_feature(
pcd_down,
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius_feature, max_nn=100))
return pcd_down, pcd_fpfh- ダウンサンプリングをして密度を揃える
- 法線を計算
- FPFH特徴量の計算
グローバルな位置合わせ
def execute_global_registration(source_down, target_down, source_fpfh,
target_fpfh, voxel_size,flag):
distance_threshold = voxel_size * 1.5
print(":: RANSAC registration on downsampled point clouds.")
print(" Since the downsampling voxel size is %.3f," % voxel_size)
print(" we use a liberal distance threshold %.3f." % distance_threshold)
result = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_ransac_based_on_feature_matching(
source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh, True,
distance_threshold,
o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPoint(flag),
3, [
o3d.pipelines.registration.CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnEdgeLength(
0.9),
o3d.pipelines.registration.CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnDistance(
distance_threshold)
], o3d.pipelines.registration.RANSACConvergenceCriteria(100000, 0.999))
return result
ローカルな位置合わせ
def execute_local_registration(pcd_tar,pcd_acc,threshold):
# ICPによる位置合わせ
trans_init = np.identity(4)
obj_func = o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPoint()
result = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_icp( pcd_tar, pcd_acc,
threshold,
trans_init,
obj_func
)
print("finish icp")
return result
結果
グローバルな位置合わせの後
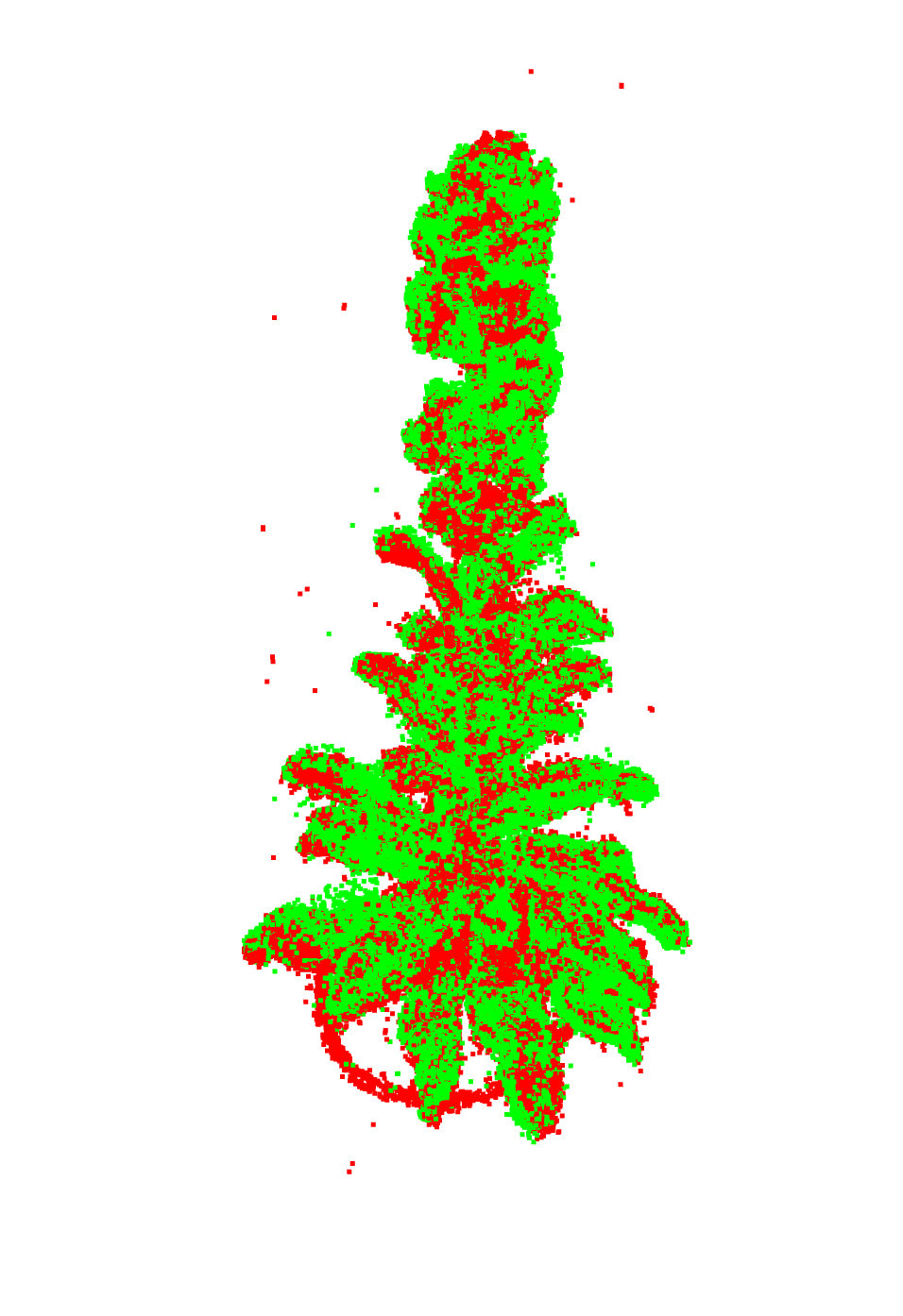

RMSE of all inlier
0.006518986586785577
低いほど精度が良い
ローカルな位置合わせの後
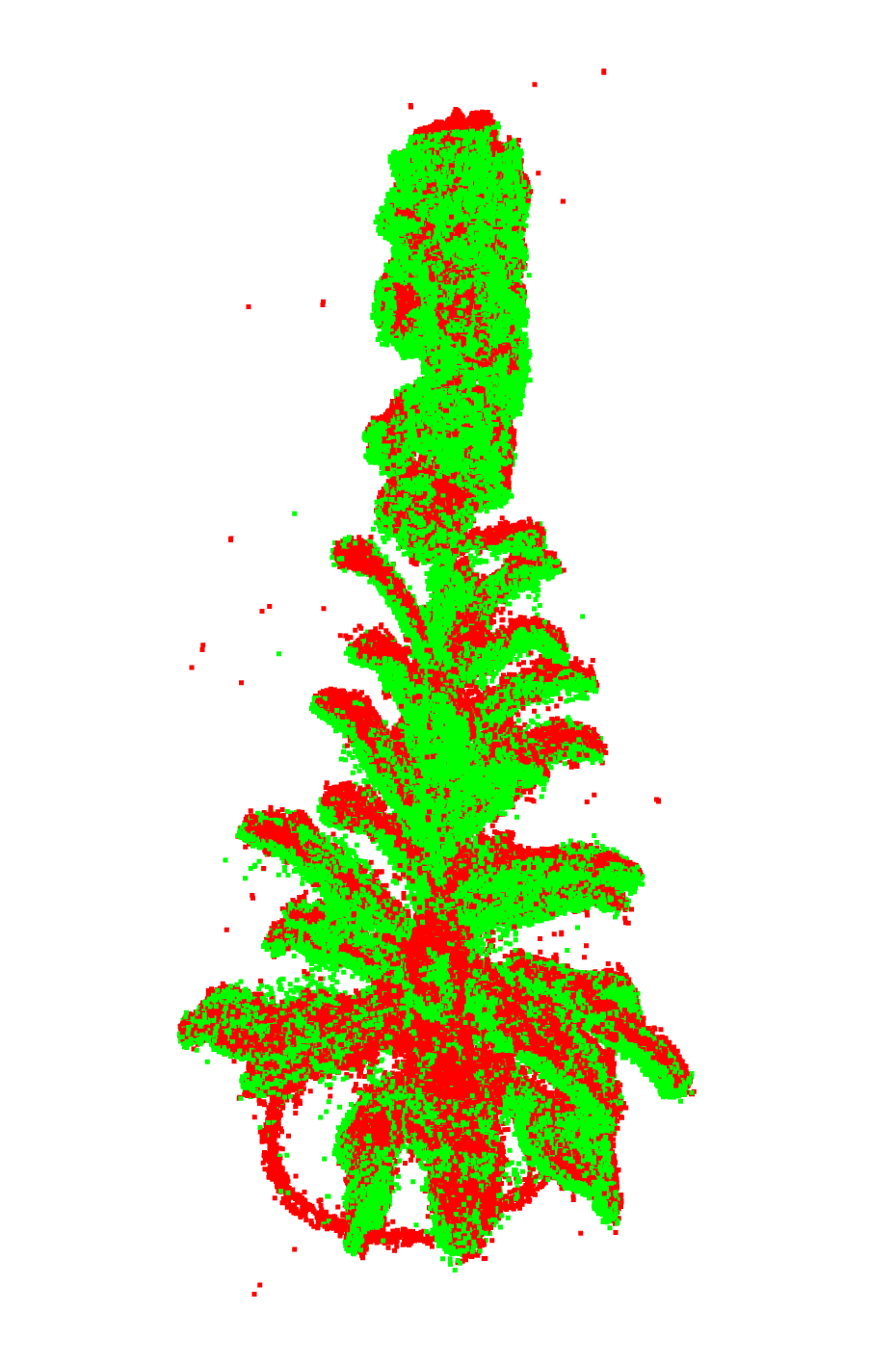
RMSE of all inlier
0.006247441569559895
まとめ
- open3d を用いて点群の位置合わせを実装できた
- RANSACを用いたレジストレーションでも十分なほど位置が合うが、それに加えICPを用いた方がより精度が良いことが確認できた
今後
- 細かいパラメータについて追う
- 撮影範囲が異なるもののレジストレーションを行ってみる